Steps to install the kubernetes cluster manually using CENTOS 7
Kubernetes is an open-source container management system. The platform provides a means for the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications across a cluster of computers. In this blog, we will show you the easier steps to install the kubernetes cluster manually using CENTOS 7.
Requirements
- 3 Virtual Machines with an internet connection.
- Kubernetes components
Overview
- Before moving on to the installation of K8s using CentOS it is mandatory to learn about the overview of Kubernetes overview and its architecture.
Infrastructure Overview
- For this installation demo, we are going to create two-node clusters.
- Here, the Master IP address will be 192.168.3.81.
- The Node 1 IP will have 192.68.3.82 and the Node 2 IP will have 192.168.3.83.
- We are using the Flannel Network for the POD communication in this demo.
Note: The VM IP’s may change based on your environment
Master server configuration
- Log in to the master server and we have already set the hostname as k8s-master during OS installation.
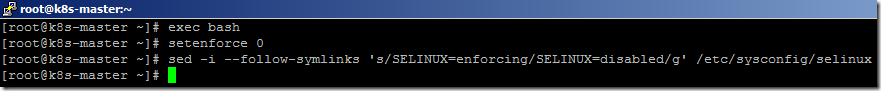
- Disable the SELinux using the below commands.
exec bash
setenforce 0
sed -i --follow-symlinks 's/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g' /etc/sysconfig/selinux
- Now, open the sysctl.conf file.
vi /etc/sysctl.conf
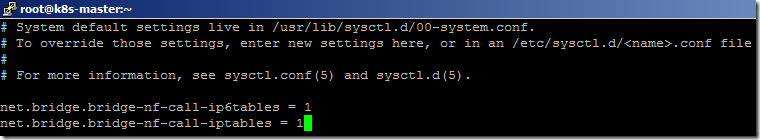
- Add the below entries in the conf file to change the Linux host bridge values and save the changes.
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
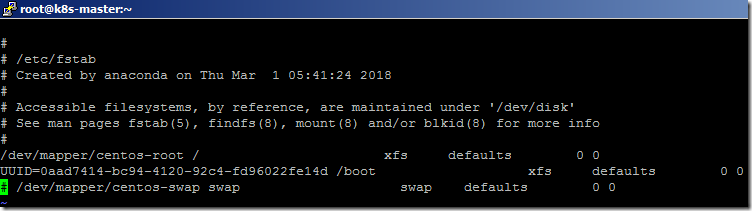
- open the fstab file.
vi /etc/fstab
- Disable the SWAP by adding the # symbol at the beginning and save the changes.
.
- Restart the VM using the command init 6 to apply the SELinux and SWAP changes.
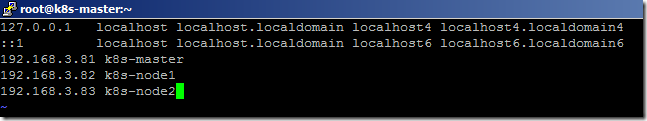
- Once the VM is back online, open the host file.
vi /etc/hosts
- Add the below entries in the host file and save the changes.
192.168.3.81 k8s-master
192.168.3.82 k8s-node1
192.168.3.83 k8s-node2
Note: The IP’s may change based on your environment
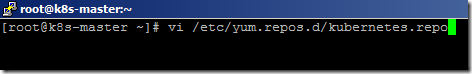
- Create a new file named kubernetes.repo under yum.repos.d folder using the below command.
vi /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo
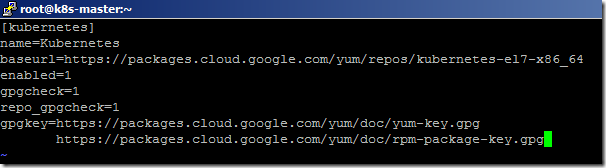
- Add the below entries and save the changes.
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
repo_gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
Installing docker and kubeadm
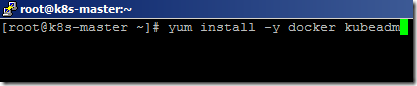
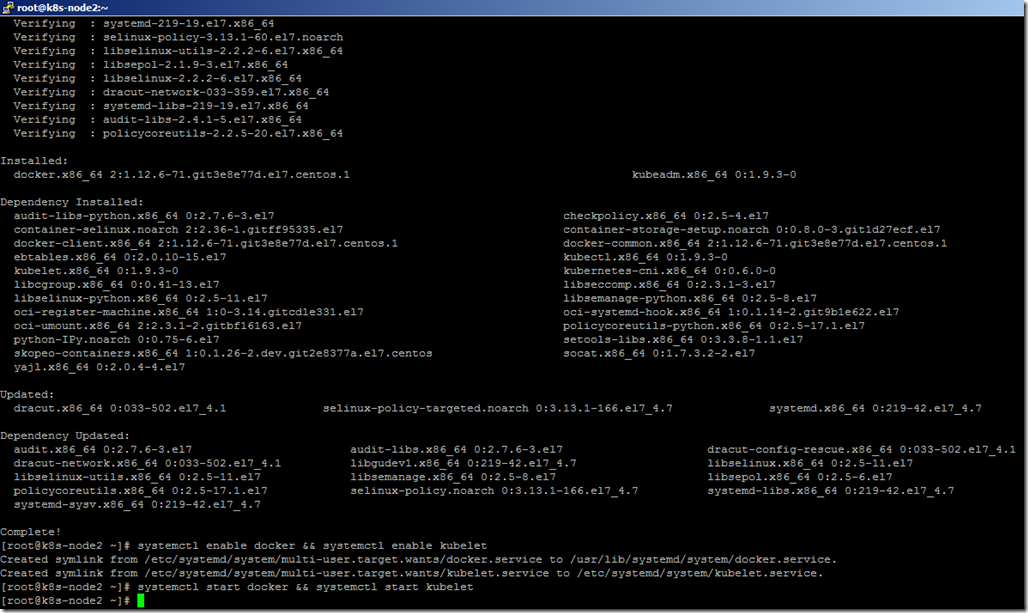
- Now, Install the docker and kubeadm using the below command.
yum install -y kubeadm docker
- It will take a few minutes to complete the installation.
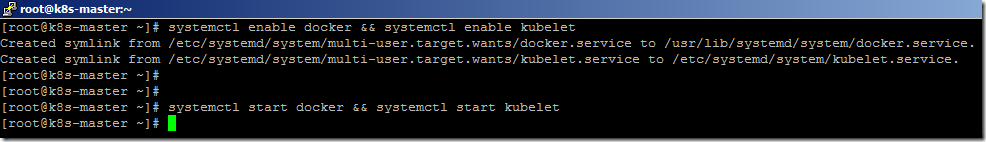
- Enable and start the docker and kubelet services using commands.
systemctl enable docker && systemctl enable kubelet
systemctl start docker && systemctl start kubelet
Node configuration
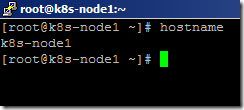
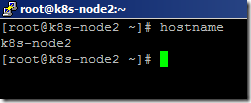
- We have already set the hostname for node1 and node2 during OS installation.
- Please follow the above master server configuration steps for the kubernetes node preparation. We have already installed the docker and kubeadm on both nodes.
Creating cluster
- We are using the Flannel network for this demo.
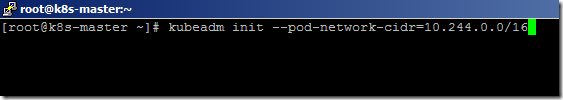
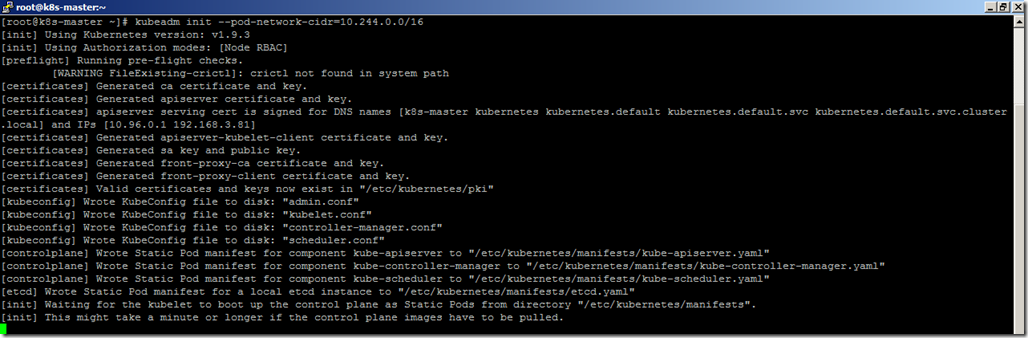
- To make the flannel to working properly, we need to specify the network CIDR while configuring the cluster. Use the below command to create a cluster.
kubeadm init --pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16
- It will take a few minutes to complete the configuration process.
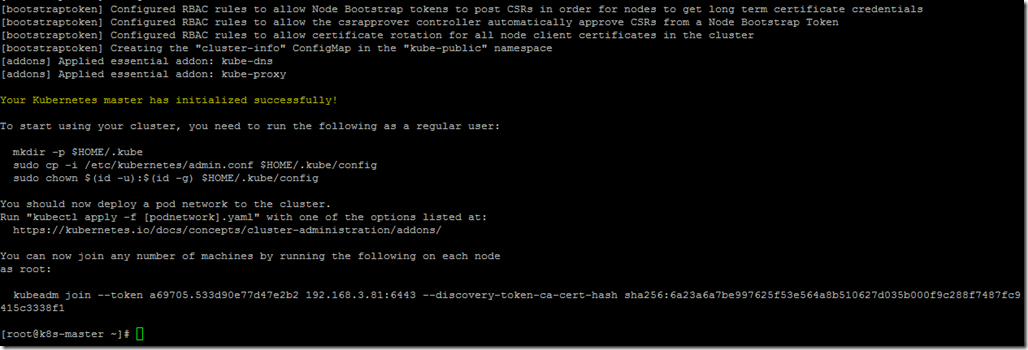
- The kubernetes cluster has been configured successfully.
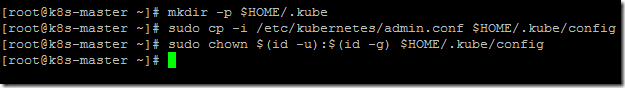
- Execute the below commands below start using the cluster.
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
- Also, make a note of the kubeadm join command to add the nodes into the cluster.
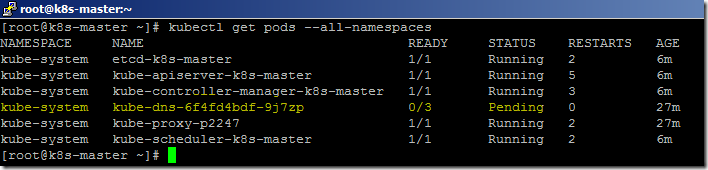
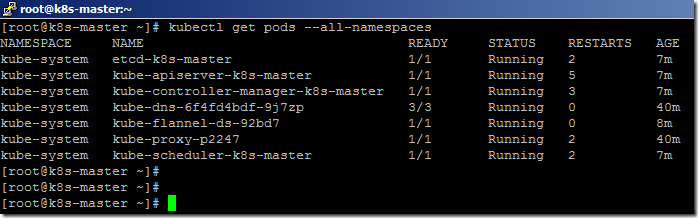
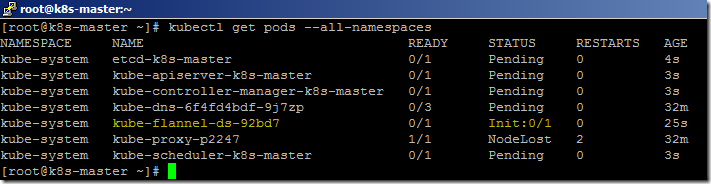
- We can list the available system PODS using the below command.
kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
- Kube-DNS will be in a pending state until we install the POD network for the cluster.
Installing network
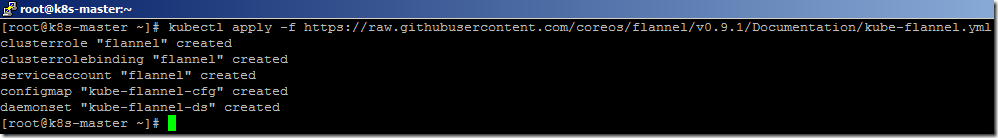
- Use the below command to install the Flannel network.
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/v0.9.1/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
- It will take a few minutes to complete the installation.
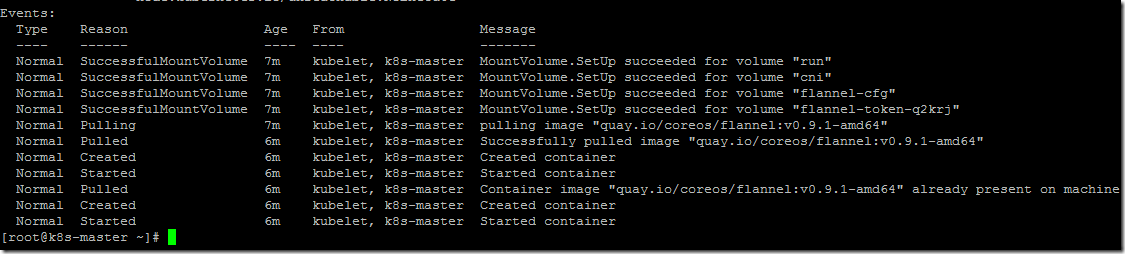
- The flannel pod will start initiating and it will take a few minutes to complete the configuration process.
- We can get detailed information about a POD using the describe option.
kubectl describe pod <pod name> --namespace=kube-system
- After some time, all the system pods are in a running state.
Adding nodes to the cluster
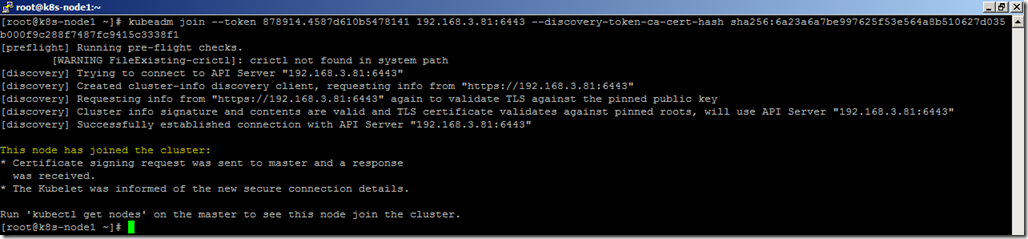
- From node1 use the kubeadm join command to add the nodes into the cluster.
kubeadm join --token 878914.4587d610b5478141 192.168.3.81:6443 --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:6a23a6a7be997625f53e564a8b510627d035b000f9c288f7487fc9415c3338f1
Note: Token ID, IP, and sha256 details will vary based on your environment
- Node has been joined into the cluster successfully.
Verification
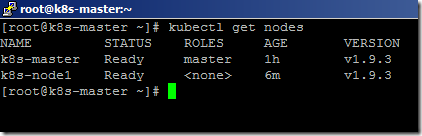
- From the master server, type the below command to list the available nodes in the cluster.
kubectl get nodes
- We can use the same kubeadm join command to add more nodes in the future.
- In case you forget to make a note of Kubeadm join information, use the below command from the master server to retrieve the join information.
kubeadm token create --print-join-command
Video Tutorial
Thank you for taking the time to read our blog on “How to install the K8s cluster manually using CentOS7?“. We hope you found the information valuable and insightful. If you find any issues with the information provided in this blog don’t hesitate to contact us (info@assistanz.com).
Optimize your kubernetes and never lose a valuable customer again!
Our mission is to ensure that your containers remain lightning-fast and protected at all times by monitoring and maintaining it 24×7 by our experts.
Related Post
How to set up a HAProxy load balancer in Ubuntu 20.04?
How to create a custom namespace in the K8s environment?